A classroom blog of homework, upcoming assignments, a calendar, and other useful things for my students.
Tuesday, December 17, 2013
Sunday, December 8, 2013
Cell Micro Study Guide
C - Level
1.
2. Eukaryote - plant or animal cell; Prokaryote - bacteria
3. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from a high concentration to a low concentration until both are equal.
B - Level
1. Prokaryote - no nucleus, no organelles, smaller, circular DNA; Eukaryote - nucleus, contains organelles, big
2. Animal cell - contains lysosome, cell membrane only, small vacuole if any, mitochondria only - uses food for energy; Plant cell - contains large vacuole, contains chloroplast (uses sunlight for energy) and contains both cell wall and cell membrane
3. See notes on organelles.
4. Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a membrane
5. No energy - osmosis, diffusion, facilitated diffusion; Energy needed - endocytosis, exocytosis, active transport
A - Level
1. See above
2. See notes.
3. Review cell metaphor
4. See #2 in BLevel
5. Discuss osmosis, diffusion, endocytosis, exocytosis
6. proteins allow large molecules to pass through membranes or allow membranes to move against the gradient (low concentration to high)
Good to know
1. lipids and proteins
2. proteins
3. bacteria, plant
4. lysosome
5. cell wall, chloroplast
6. ribosome
7. shrink
8. plant and bacteria
9. lysosome
10. both are involved in generating energy for the organism. Chloroplasts generate energy from sun, water and carbon dioxide. Mitochondria generate energy from food.
1.
2. Eukaryote - plant or animal cell; Prokaryote - bacteria
3. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from a high concentration to a low concentration until both are equal.
B - Level
1. Prokaryote - no nucleus, no organelles, smaller, circular DNA; Eukaryote - nucleus, contains organelles, big
2. Animal cell - contains lysosome, cell membrane only, small vacuole if any, mitochondria only - uses food for energy; Plant cell - contains large vacuole, contains chloroplast (uses sunlight for energy) and contains both cell wall and cell membrane
3. See notes on organelles.
4. Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a membrane
5. No energy - osmosis, diffusion, facilitated diffusion; Energy needed - endocytosis, exocytosis, active transport
A - Level
1. See above
2. See notes.
3. Review cell metaphor
4. See #2 in BLevel
5. Discuss osmosis, diffusion, endocytosis, exocytosis
6. proteins allow large molecules to pass through membranes or allow membranes to move against the gradient (low concentration to high)
Good to know
1. lipids and proteins
2. proteins
3. bacteria, plant
4. lysosome
5. cell wall, chloroplast
6. ribosome
7. shrink
8. plant and bacteria
9. lysosome
10. both are involved in generating energy for the organism. Chloroplasts generate energy from sun, water and carbon dioxide. Mitochondria generate energy from food.
Thursday, November 21, 2013
Wednesday, October 30, 2013
Ecology Study Guide 2
This study guide is due FRIDAY (November 1).
- Mutualism - Both organisms benefit from the relationship.
- Commensalism - One organism benefits and the other does not benefit and is not harmed.
- Parasitism - One organism benefits while the other is harmed.
- Whale and Barnacle; Eyelash Mite and Humans; Sea Cucumber and Fish
- Birth Rate, Death Rate, Emigration, Immigration
- Katrina moved from San Diego to San Jose. She emigrated from San Diego. She immigrated to San Jose.
- The squirrel would eat more producers. Competition among the species would increase.
- Water, Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus
- Bacteria
- Urine and Decomposition
- Animals and Plants that lived millions of years ago.
- solar, wind, water
- coal, oil, natural gas
- Due to technology, we are able to create more food (resources) than ever before. This allows us to support more living things.
- Agriculture, building cities, transportation, industries
- Often time it's inconvenient and costly
- Global warming occurs when the atmosphere thickens due to increased carbon emissions (from transportation and industry) This thicker atmosphere traps the heat from the sun and causes the earth to heat up.
- Primary succession begins on bare rock
Thursday, September 26, 2013
Ecology (Test 1) Study Guide Answers
- Individual - one organism; Population - a group of the same organism; Community - all living (biotic) factors in an area; Ecosystem - all the living and nonliving (abiotic) factors in an area; Biome - similar ecosystems (example: desert, tundra, rainforest); Biosphere - where all life exists on earth.
- (we'll go over this in class)
- (we'll go over this in class)
- population, abiotic factors, ecosystem, biosphere, biotic factors
- A food web shows ALL of the feeding relationships within an ecosystem. A food chain only shows a partial (linear) pathway of energy.
Predator Prey Relationship
- Increasing
- Increasing
- As the moose population increased, there was more food available for the wolves which in turn resulted in the increase of the wolf population.
Sunday, September 8, 2013
Unit 1 Study Guide Answers
- Hair is tied back
- Closed toed shoes
- No loose clothing
2.
- Run water over your skin for at least 5 minutes.
3. Gram
4. Meter
5. Liter
6. 0.00352 km
7. 24L = 24 L (this was a typo - sorry!)
8. a. 1 cm
b. 1 KL
c. 10 g
9. a. coffee
b. time to complete problems
c. group b (no special treatment)
d. they complete the same problems, same age, same level of math
10. a. Does drinking milk affect growth rate?
b. Milk causes increased growth.
c. 10 randomly chosen babies with the same birthdate. After they turn 5 years old, Group drinks 2 cups of milk every day. Group B drinks 2 cups of water instead. Measure growth after 10 years.
11. cohesion (water sticking to itself)
12. high specific heat (water's ability to absorb heat)
13. adhesion - water sticking to other molecules; cohesion - water sticking to other water molecules.
Friday, May 31, 2013
2nd Semester Study Guide Answers
1. Differentiate between
a. Homozygous & Heterozygous - Homozygous 2 copies of the same allele; Heterozygous 2 different copies of the allele
b. Dominant & Recessive - Dominant, usually a capital letter always shows up when present; Recessive, usually a lower case letter, only shows up when there are two copies of it
c. RNA & DNA - DNA has two strands, thymine (T), and deoxyribose, RNA has one strand, uracil (U), and ribose
d. Genes & alleles - genes - DNA that codes for a physical trait; alleles - different forms of a gene
e. Haploid & diploid - Haploid - sex cells, cells with one copy of chromosomes; Diploid - body cells, cells with 2 copies of chromosomes
f. Transcription & translation - transcription mRNA copying DNA; translation - mRNA translated into amino acids
g. positive feedback & negative feedback - positive feedback - brain pushes body farther away from normal before going back; negative feedback - brain brings body back to normal right away
h. arteries & veins - arteries bring blood away from the heart; veins bring blood back to the heart.
2.
a. Homozygous & Heterozygous - Homozygous 2 copies of the same allele; Heterozygous 2 different copies of the allele
b. Dominant & Recessive - Dominant, usually a capital letter always shows up when present; Recessive, usually a lower case letter, only shows up when there are two copies of it
c. RNA & DNA - DNA has two strands, thymine (T), and deoxyribose, RNA has one strand, uracil (U), and ribose
d. Genes & alleles - genes - DNA that codes for a physical trait; alleles - different forms of a gene
e. Haploid & diploid - Haploid - sex cells, cells with one copy of chromosomes; Diploid - body cells, cells with 2 copies of chromosomes
f. Transcription & translation - transcription mRNA copying DNA; translation - mRNA translated into amino acids
g. positive feedback & negative feedback - positive feedback - brain pushes body farther away from normal before going back; negative feedback - brain brings body back to normal right away
h. arteries & veins - arteries bring blood away from the heart; veins bring blood back to the heart.
2.
- camouflage
- padded feet for running
- muscular build to hunt
3. genetic, population, time
4. variation creates competition. without variation, there would be no competition for survival
5. Sam and his friends have long necks due to their genes. Because of that, they ate better than other tortoises and passed on their genes.
6. 46
7. 2
8. 75%
9. 50% (it's always 50%)
10. A trait that is on the X-Chromosome
11. colorblindness, hemophilia
12. 0%, 0%
13. a. Red; b. red & white; c. orange (or any other color that is not red or white)
14. (ask Mrs. Sohn in class)
15. half of the original is saved to make the new strand
16. DNA - ATCG; RNA- AUCG
17. A-T; C-G
18. mRNA
19. tRNA
20. a. GCG ATA CTC AAT; b. TAC GCA CTA GCT
21. a. UCC CCG GGA AAU; b. GAU AGU CUU GGA
22. 3 bases that code for an amino acid
23. 15
24. C, B, D, A
25. dendrites receive signal from another neuron;
26. holds the signal inside the axon
27. pain killers block receptors
28. chemicals that are released into the blood stream that cause changes in the body
29. both are involved in communication inside the body
30. alveoli
31. body is alerting you to danger; example - spider bite that swells and gets increasingly painful
32. 4
33. 1st line of defense - skin, hair, mucous; 2nd line - white blood cell, inflammatory response
34. antibodies pull the different pathogens together to be eaten by a white blood cell
35. they force your body to develop T-cells that are targeted to fight the pathogens
36. HIV - virus infection; AIDS - when T-cell counts drop to a very low level
37. energy available in food
38. Condoms
39. prevent ovulation; prevents fertilized egg from implanting in the uterus
40. (various - HIV, herpes, chlamydia)
Thursday, April 4, 2013
Evolution Study Guide Answers
- Variation
- Natural Selection
- Evolution
- Genes
- Adaptation
- Fitness
- Genetic Drift
- Half-life
- Alelle Frequency
- Speciation
- Founder's Effect
- Relative Dating
- Nocturnal (to avoid heat); No fur (to stay cool); Animals are really good at extracting water from food (no need to drink)
- Because the trees were covered in soot, the once favored light moths suddenly stood out against the dark trees. This made them a more likely target for predators. This caused a rapid change in the genes of the moths. More dark genes were now present in the peppered moth population.
- (Left to Right, Top to Bottom): 4, 2, 5, 3,1,6,
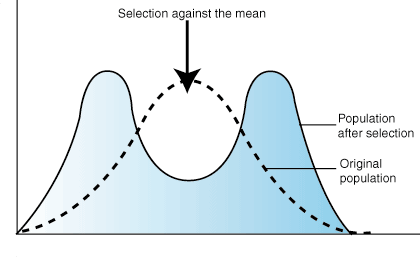
 graph shifts to the left.
graph shifts to the left.- 10 g.
- Opposable thumbs, large brains compared to body size, binocular vision, bipedalism
- Sexual reproducers produce variation every time they produce offspring (minnows, incest = more disease)
Wednesday, March 13, 2013
Genetics Review Packet (the 4 pages of punnett squares)
- Dominant - The gene that always shows, usually a capital letter
- Recessive - The gene that is present only when the dominant gene is not present, usually a lower case letter
- 1/4 (triangle) 1:3 (circle) 75% (square)
- a. gene b. homozygous c. punnett square d. genotype e. phenotype f. ratio g. probability
- a. heterozygous b. heterozygous c. homozygous dominant d. heterozygous e. homozygous recessive f. homozygous recessive g. homozygous dominant h. heterozygous
- 25% - BB 50% - Bb 25% - bb
- 0% - BB; 50% - Bb; 50% - bb
- 1/4 BbEe (Black hair/ brown eyes); 1/4 Bbee (Black hair/ blue eyes); 1/4 bbEe (blonde hair/brown eyes); bbee (blonde hair/blue eyes)
- Parent 1 - rr and Parent 2 - Rr; (rr x Rr) 50% White, 50% Pink
- Males (XY); Females (XX)
- Cross XY and XX
- a. 100% Type O; b. 100% Type AB; c. 50% Type A, 50% Type B
- a. 2/2 girls with normal vision, 1/2 normal boys, 1/2 boys colorblind; b. 2/2 girls are normal, 2/2 boys are colorblind; c. 2/2 girls are normal, 2/2 boys are normal
Genetics Study Guide Answer
This was today's hand out:
C - Level
1. C. AABbcc will look the same as AaBBcc
2. Meiosis - makes sex cells, 4 genetically different cells; Mitosis – makes every other cell, 2 genetically identical cells
3. Tt x Tt = 75% will look like T, 25% will look like t
4. Incomplete Dominance (3rd phenotype appears)
5. XHXh with XHY
a. Daughters with hemophilia – 0%
b. Sons with hemophilia – 50%
6. Two organisms may share the same phenotype, but have differing genotype.
7. Bb x Bb (75% Black, 25% Brown fur)
8. To make genetically different cells
9. Sex cells are also known as gametes. Since they only have 1 set of chromosomes, they are called haploid. Cells with 2 sets of chromosomes are called diploid.
10. 2 brothers!
B – Level
1. Incomplete dominance
a. RR – red, rr – white, Rr – pink.
b. rr x Rr = 50% white, 50% pink
2. Key: BB – blue, bb – white, Bb – blue AND white. Bb x Bb = 25% Blue, 25% white, 50% blue and white.
3. ii x IAIB = 50% Type A, 50% Type B
4. (check with Mrs. Sohn in class)
5. XBXB with XbY
a. 0% sons will be colorblind
b. 0% of daughters will be colorblind
6. Key: D – Dark, d – blonde
a. Dd
b. dd
c. 50%
A – Level
1. Dihybrid Cross
a. BbEe
b. bbee
c. ¼
d. ¼
2. Males are more likely to inherit sex-linked traits because they only have one X. If there is something wrong with that X, they will always show the trait. They do not have another X to “make up” for that other X.
3. ii x ii; IAi x IAi, IBi x IBi
C - Level
1. C. AABbcc will look the same as AaBBcc
2. Meiosis - makes sex cells, 4 genetically different cells; Mitosis – makes every other cell, 2 genetically identical cells
3. Tt x Tt = 75% will look like T, 25% will look like t
4. Incomplete Dominance (3rd phenotype appears)
5. XHXh with XHY
a. Daughters with hemophilia – 0%
b. Sons with hemophilia – 50%
6. Two organisms may share the same phenotype, but have differing genotype.
7. Bb x Bb (75% Black, 25% Brown fur)
8. To make genetically different cells
9. Sex cells are also known as gametes. Since they only have 1 set of chromosomes, they are called haploid. Cells with 2 sets of chromosomes are called diploid.
10. 2 brothers!
B – Level
1. Incomplete dominance
a. RR – red, rr – white, Rr – pink.
b. rr x Rr = 50% white, 50% pink
2. Key: BB – blue, bb – white, Bb – blue AND white. Bb x Bb = 25% Blue, 25% white, 50% blue and white.
3. ii x IAIB = 50% Type A, 50% Type B
4. (check with Mrs. Sohn in class)
5. XBXB with XbY
a. 0% sons will be colorblind
b. 0% of daughters will be colorblind
6. Key: D – Dark, d – blonde
a. Dd
b. dd
c. 50%
A – Level
1. Dihybrid Cross
a. BbEe
b. bbee
c. ¼
d. ¼
2. Males are more likely to inherit sex-linked traits because they only have one X. If there is something wrong with that X, they will always show the trait. They do not have another X to “make up” for that other X.
3. ii x ii; IAi x IAi, IBi x IBi
Tuesday, February 5, 2013
Protein Synthesis Study Guide
C-Level
- CTT CAT CTG ACA
- ACG AUA AGU CCC
- 4 - (Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine)
- Double Helix
- Nucleus
- C. Proteins
- DNA - 2 strands, RNA - 1 strand
- met - gly - trp - ser - stop
B&A Level
- RNA - ribose, uracil; DNA - deoxyribose, thymine
- 3
- mRNA
- mRNA copies one side of the DNA to get the recipe to make the protein
- the mRNA is translated one codon at a time into an amino acid chain
- a change in DNA
- mutations can cause a change in the type of protein produced
- UCA - serine; UCG - also serine. This mutation resulted in the same amino acid created.
- D
- nucleus
- ribosome
- amino acids
- (see notes)
- mRNA is copying one side of the DNA in the nucleus.
- mRNA leaves nucleus and is translated into amino acids in the ribosome.
Monday, January 14, 2013
Tuesday, January 8, 2013
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)